NIH Infant and Toddler “Baby” Toolbox
Contains more than 30 assessments of Cognition, Motor, and Social-Emotional domains in one iPad app. Our valid, reliable, and norm-referenced measures allow for assessment of children throughout infancy and early childhood (ages 0 to 42 months).
Development at a Glance
In response to demand for a more portable assessment system, Version 2 of the NIH Toolbox launched to researchers and clinicians on the App Store for iPad.
The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development awarded the NIH Baby Toolbox contract to Northwestern University using NIH Blueprint funds. Dr. Richard Gershon, Principal Investigator, and a team of 48 researchers started work to develop a brief, standardized assessment of neuropsychological, cognitive and social assessment of infants and toddlers ages 1-42 months.
NIH Baby Toolbox began early validation.
Collected validation and normative data for the NIH Baby Toolbox tests aligned with the U.S. Census.
The analytics team for the NIH Baby Toolbox is developing scores and norms for the iPad-based tests. Public release is expected in the second half of 2024.
Key Features in the NIH Baby Toolbox
Modern UX/UI Capabilities consistent with the Toolbox Systems
User-friendly administration
Gaze-based preferential looking tasks
Normative scores from 1-42 months
Multi-method assessment modalities
Overview of Development
The NIH Baby Toolbox app assesses key developmental domains. Candidate measure selection was informed by input from an expert survey of developmental clinicians and researchers and a scoping review of over 30,000 manuscripts. Potential tests were reviewed for the ease of tablet-based administration and scoring, likelihood of standardization, scientific value, and ability to present stimuli in both English and Spanish. In this way, the Baby Toolbox tests were adapted from existing measures and laboratory-based paradigms, common among developmental researchers.
Key to the NIH Baby Toolbox is an emphasis on modern measurement methods. These methodologies include utilization of gaze-based preferential looking paradigms, on-device video recording and playback, and reporting functionality. To ensure the success of these developments, all of the NIH Baby Toolbox measures went through multiple stages of pilot testing and refinement. This includes feasibility testing new technology (e.g., four rounds of gaze-based pilot tests), evaluation of convergent validity between candidate Baby Toolbox measures, and existing developmental tests, as well as a comprehensive “dry run” of the entire battery.
In preparation for the NIH Baby Toolbox release, a comprehensive norming study was conducted. Over 2,500 infants and toddlers from English- and Spanish-speaking households between the ages of 1 and 48 months were recruited across the country. Participant demographics were matched to the US Census for language spoken at home, race, ethnicity, sex assigned at birth, parental education, and geographic census region. Concurrent with the norming study, test-retest reliability and convergent validity studies were also conducted.
The NIH Baby Toolbox app is programmed using a similar user interface as the NIH Toolbox Version 3, which incorporates input from usability and accessibility experts to enhance its user experience for both examiners and participants. Users will find an easy-to-navigate interface, allowing for easy selection and administration of tests. Once the assessment is complete, results can be accessed through a Score Report or .CSV file designed for easy importing into research and clinical databases.
Cognition
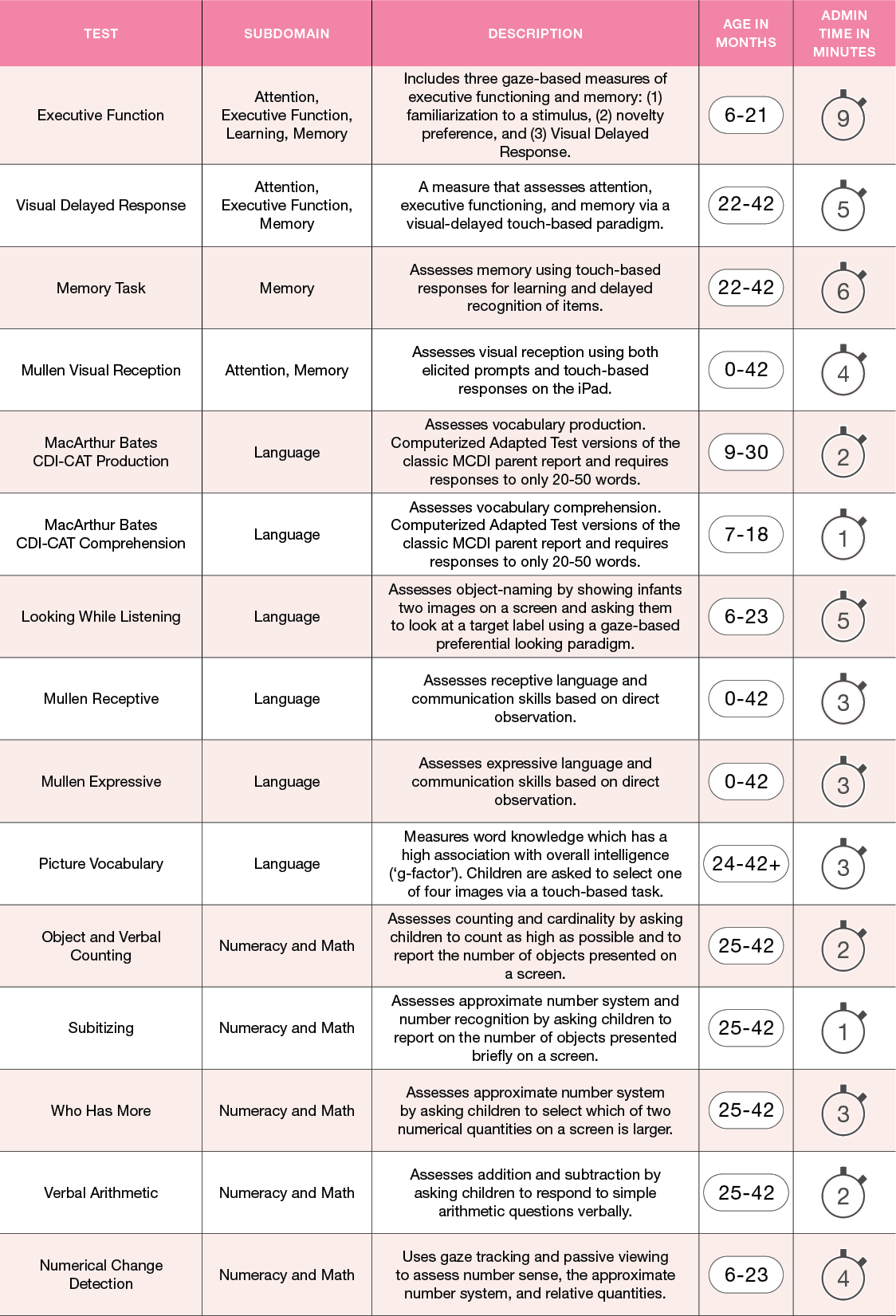
Cognition refers to the mental processes involved in attention, executive functioning, gaining knowledge, and comprehension, such as thinking, knowing, remembering, judging, and problem solving.
Through gaze-based and touch-based tasks on the iPad, behavioral observation, and parent report, the NIH Baby Toolbox Cognition domain produces individual measure-level scores and composite scores. Supplemental tests are not used in the calculation of composites but can be administered to better understand the participant’s cognitive functioning.

Cognition Tests
Social-Emotional Functioning
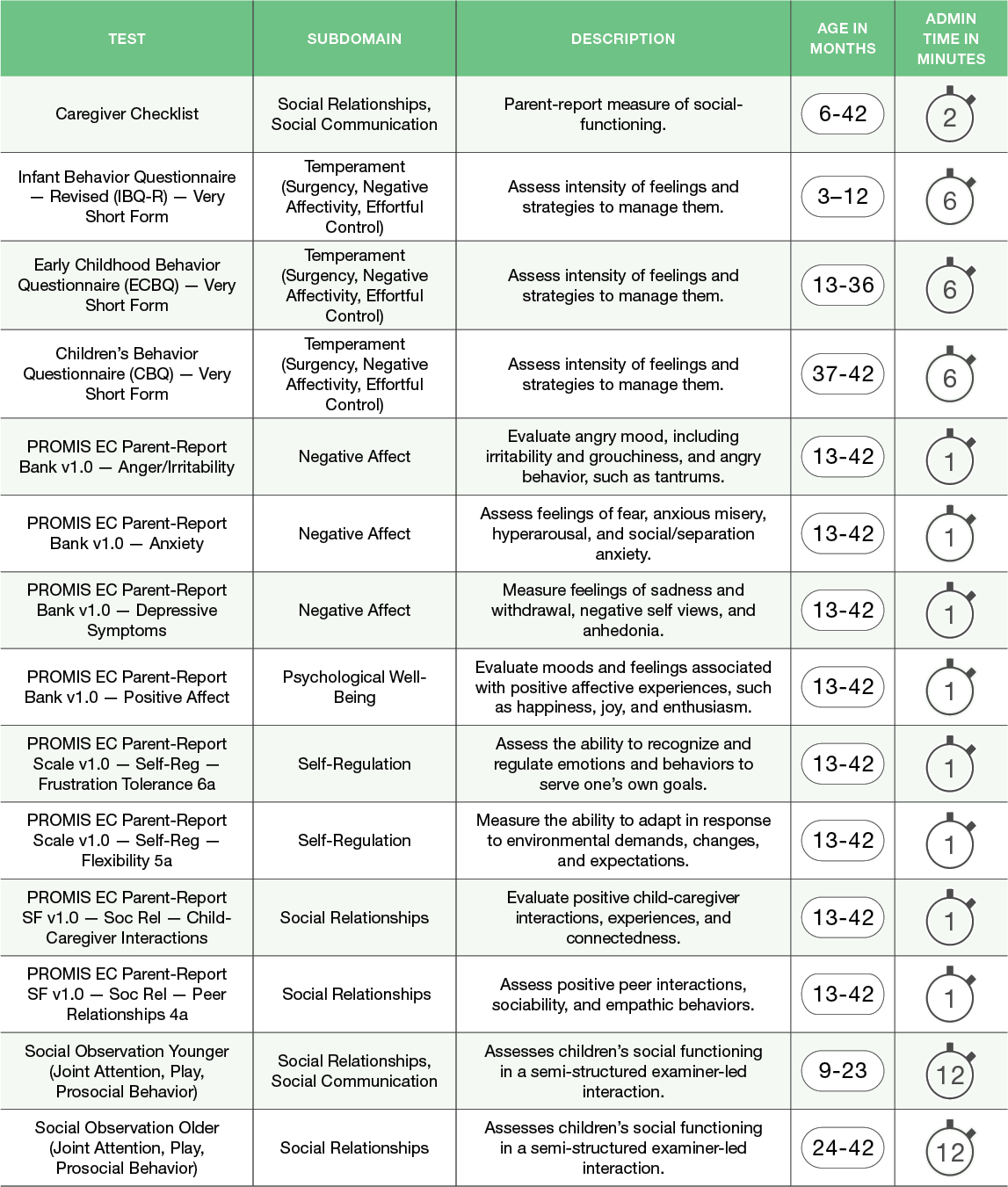
Social-Emotional functioning refers to the social competencies related to the perception/recognition of others, social responsiveness/reciprocity, positive social interactions and communication, and relationships with adults and peers. It also covers the experience, expression, and management of any strong feelings (i.e., emotions), such as excitement, fear, or anger.
Early social-emotional functioning is foundational for lifelong health and well-being. Social-Emotional functioning is assessed in the NIH Baby Toolbox through behavioral observation and parent proxy report.

Social-Emotional Functioning Tests
Motor Functioning
Motor function involves complex physiological processes and requires the integration of multiple systems, including neuromuscular, musculoskeletal, cardiopulmonary, neural motor and sensory-perceptual systems.
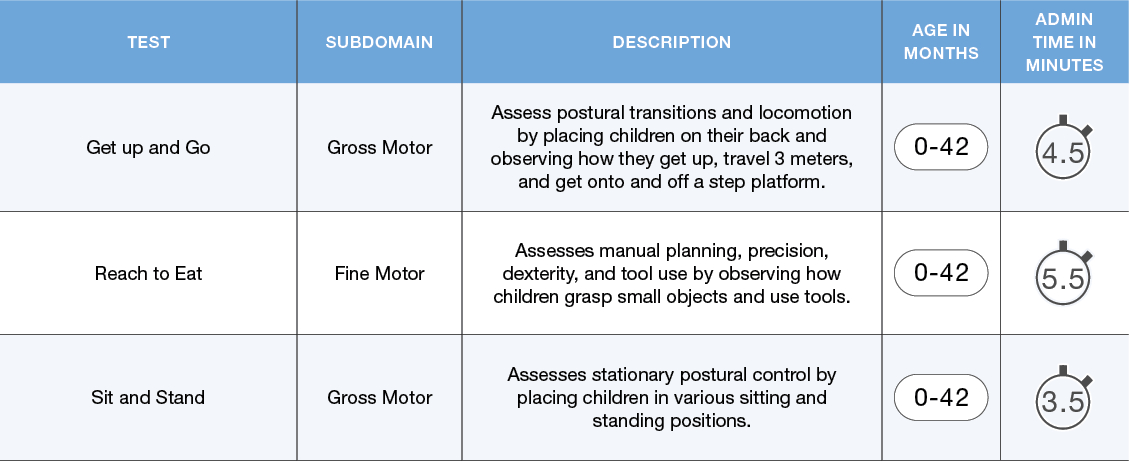
The NIH Baby Toolbox motor measures assess both Fine Motor and Gross Motor abilities.

Motor Functioning Tests